The prostate is crucial to men’s health. This gland, often enshrouded in obscurity, plays a pivotal role. This article delves into the multifaceted functions of the prostate, highlighting its significance in the male reproductive system and overall well-being.
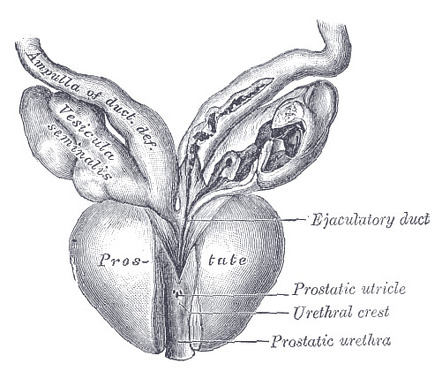
Anatomical Overview of the Prostate
Nestled below the bladder, the prostate is a walnut-sized gland integral to the male reproductive system. Its size and structure evolve with age, underscoring the dynamic nature of this organ. The prostate surrounds the urethra, the duct through which urine and semen exit the body, making its health crucial for urinary and reproductive functions.
The Prostate’s Role in the Reproductive System
The prostate’s primary function lies in its contribution to seminal fluid, a critical component of semen. This fluid nourishes and transports sperm, playing a vital role in fertility. During ejaculation, the prostate’s muscular fibers contract, facilitating the expulsion of semen, a process vital for reproduction.
Hormonal Influence on the Prostate
Testosterone and other androgens exert a profound influence on the prostate. These hormones regulate its growth and function, with their levels and interactions playing a crucial role throughout a man’s life. The balance of these hormones is crucial; imbalances can lead to various prostate-related health issues.
Common Prostate Conditions
Men often encounter prostate-related conditions such as Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), characterized by an enlarged prostate, and Prostatitis, an inflammation of the gland. Prostate cancer, a significant health concern, stands as a leading cause of cancer in men. Understanding these conditions is key to early detection and effective management.
Symptoms of Prostate Disorders
Symptoms like urinary difficulties, discomfort during urination, and a frequent need to urinate, especially at night, signal potential prostate issues. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for timely medical intervention.
Diagnostic Methods for Prostate Health
Prostate health assessment involves Digital Rectal Exams (DRE), where a physician feels the prostate for abnormalities, and Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) blood tests, which can indicate the presence of prostate cancer. In some cases, imaging and biopsies are necessary to ascertain the presence of abnormalities or malignancies.
Preventive Measures for Prostate Health
Adopting a healthy diet and lifestyle, coupled with regular screenings, can markedly reduce the risk of prostate disorders. Foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids are particularly beneficial, while regular exercise can significantly improve prostate health.
Treatment Options for Prostate Conditions
Treatment modalities range from medications for BPH and prostatitis to surgical and advanced therapeutic interventions in cases of prostate cancer. The choice of treatment depends on the severity and nature of the condition, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences.
The Prostate and Sexual Health
The prostate’s health directly impacts sexual functions, with disorders often leading to erectile dysfunction and altered sexual experiences. The prostate’s role in ejaculation also means that its health is crucial for a satisfying sexual life.
The Psychological Impact of Prostate Disorders
A diagnosis of prostate disease can be psychologically taxing, necessitating a focus on mental health alongside physical treatment. Support groups and counseling can be beneficial for those dealing with prostate health issues.
Nutrition and the Prostate
Certain foods are known to bolster prostate health, while others may elevate risk factors. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains is key in maintaining a healthy prostate.
Exercise and Prostate Health
Regular physical activity positively affects prostate health, with specific exercises recommended to enhance prostate function. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling are particularly beneficial.
The Aging Prostate
As men age, the prostate undergoes changes, making age a significant factor in prostate health management. Regular screenings become increasingly important as men enter their 50s and beyond.
The Prostate and Urinary Function
The prostate plays a vital role in urinary control, with prostate issues often manifesting as urinary symptoms such as incontinence or difficulty urinating.
Myths and Misconceptions About the Prostate
Common myths surrounding the prostate are debunked, providing clarity on this often-misunderstood gland. For instance, not all prostate enlargement is indicative of cancer, and sexual activity does not necessarily impact prostate health negatively.
The Role of Genetics in Prostate Health
Genetic predisposition plays a role in the likelihood of developing prostate conditions, with genetic testing emerging as a tool in prostate health management. Men with a family history of prostate issues should be particularly vigilant.
The Impact of Lifestyle on Prostate Health
Lifestyle choices have a substantial impact on prostate health, underscoring the importance of healthy living practices. Avoiding smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy weight are all beneficial.
Future of Prostate Health Research
Ongoing research in prostate health promises new insights and treatments, offering hope for future advancements. Innovations in diagnostics, treatment, and prevention continue to evolve, improving the outlook for prostate health.
Conclusion
Understanding the prostate’s role is crucial for male health. This awareness, combined with proactive management, is key to maintaining prostate health and overall well-being. Regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and staying informed are the cornerstones of effective prostate health management.